Hope is no strategy when it comes to inflation
Consumers are the ultimate arbiter of inflation, the absolute level and the rate of growth, so what they think matters.
The concept of inflation is ethereal, communication is key and using the yardsticks that you have should be embraced as indicators of effective communication. Consumers are the ultimate arbiter of inflation, the absolute level and the rate of growth, so what they think matters.
An effective central bank sets out to anchor inflation expectations
An effective central bank sets out to anchor inflation expectations
Letting them know your inflation objectives and how you seek to achieve them expressly determines credibility in the eyes of the consumer. An effective central bank sets out to anchor inflation expectations, in Australia’s case a predefined band which is 2–3 per cent.
If there is a high degree of certainty and trust in the community around these targets being met behavior will allow for it in day-to-day decision making, CPI volatility will reduce, price stability will prevail and in turn the inflation outcome will be self-fulfilling.
Take, for example, the recent Enterprise Bargaining Agreements (EBA's) which targeted wage growth outcomes which were consistent with the rate of expected inflation i.e. 2–3 per cent. We also know as a matter of course that many workers, be they organised groups or individuals, set their own expectations off these publicly announced EBAs.
This creates an infinite and virtuous cycle of expectation equals outcome, as long as credibility is maintained. If we break this nexus we have reference points from real world examples like Japan or more recently Europe, who has the added complexity of communicating its objectives in 24 different languages, we need to avoid this at all costs. Central bank resoluteness and its communication is critical for actual outcomes.
How does a central bank measure the efficacy of its communication?
How does a central bank measure the efficacy of its communication?
Using data from other developed economies we know that only a very small percentage of the population is aware of the objectives of their respective central banks.
In the United States, surveys tell us that only approximately 25 per cent of households are aware of the Federal Reserve’s 2 per cent inflation objective. Furthermore European surveys tell us a similar story where household estimates of inflation between 2004 to 2018 were approximately 9 per cent on average when in fact inflation ran at 1.60 per cent.
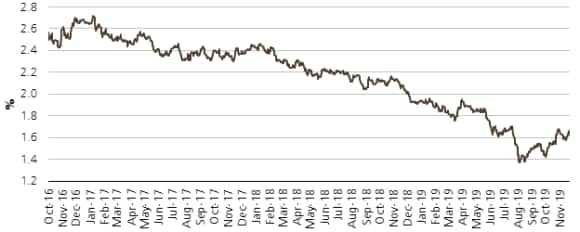
Communication and its effectiveness – as measured by these numbers clearly has a long way to go! Every expectation metric will have its flaws, but we as investors and the central banking community must take these signals seriously whilst allowing for nuance and error in all the signals that are available. As shown below, with our 20-year inflation market pointing to below target outcomes for 20 years with increased certainty, it would be wise to heed the warning it is flashing.

Christian Baylis Ph.D
Christian Baylis Ph.D
Portfolio Manager, UBS Asset Management Australia
Australian 20-year breakeven inflation rate
Australian 20-year breakeven inflation rate
Communication and its utility is growing in a world where traditional policy space reaches exhaustion. We have seen recent examples of communication tools such as forward guidance on interest rates used.
Simple announcements by central banks engender a greater degree of confidence
Simple announcements by central banks engender a greater degree of confidence
A simple announcement by a central bank that interest rates will stay where they are for an extended period engenders a greater degree of confidence when going out to buy a house or some other consumable item. Or in other words communication overrides and subordinates the signal of strong macro data which means market participants and the community become desensitized to incoming data, rather relying on the words of the central bank.
This ultimately supports the inflation objective in the short to medium term as it may bring forward or upscale a purchasing decision that may have been otherwise delayed due to uncertainty surrounding interest rates. In this case the central bank accepts the risk of higher inflation in the short term or the defined period and would opt to lean on higher inflation at a future point, rather than contemporaneously.
When interest rates are so low consumers may simply not believe they will stay there, diluting the effectiveness of interest rate policy as we get closer to the effective lower bound, so shoring up these rates by ‘communication augmentation’ becomes an ever-growing and higher utility option. The flip side to this, the feedback from market signals is less reliable as it has been heavily influenced by the communication. Balancing the tradeoff here is important.
Central banks need to now be more forthright.
Central banks need to now be more forthright.
If communication is becoming increasingly valuable central banks need to now more than before be more forthright with highly engineered plans to influence society with their plans and objectives. The take up or focus from central banks on this topic varies by some degree, with the Reserve Bank of New Zealand most likely leading the way by using press conferences and more of them alongside cartoons to help resonate with different demographics.
Look no further than recent successful political campaigns in Australia and the UK where in both campaigns the dominant form of communicating key facts and policies was via the use of memes. Particular parts of society will have different preferences for the way they consume information. As per political campaigns it could well be that the same message needs to be constructed differently for the area of the country or the multitude of demographics.
Central banks need more coordinated and sophisticated communication plans and the sooner the better. Ignore the vital signs and the road back to normalcy could be far longer than otherwise required.
Make an inquiry
Fill in an inquiry form and leave your details – we’ll be back in touch.
Introducing our leadership team
Meet the members of the team responsible for UBS Asset Management’s strategic direction.
