Are emerging markets a hot spot for sustainable investing?
As the growing trend of sustainable investing places companies with a sustainable competitive edge, we believe this could put them in a position to potentially outperform
Key takeaways
Key takeaways
- EM companies typically get low scores for ESG from traditional metrics
- In part, that’s because of lower levels of public, English language disclosure of traditional sustainability metrics in EM
- On-the-ground primary research, including regular interaction with management allow for an informed view on the fundamentals and sustainability practices long-term of a company
- Empirical evidence shows that improvements in sustainability metrics can drive market performance for EM companies
Underlying all of these sector trends is the growing importance of sustainability issues for both companies and investors in EM. Sustainability performance is derived from a company’s performance on environmental, social and governance (ESG) metrics.
A core aspect of sustainability also involves assessing the quality of a company’s management and its ability to orient the business away from material risks, toward opportunities.
EM companies = ESG laggards or lower disclosures?
EM companies = ESG laggards or lower disclosures?
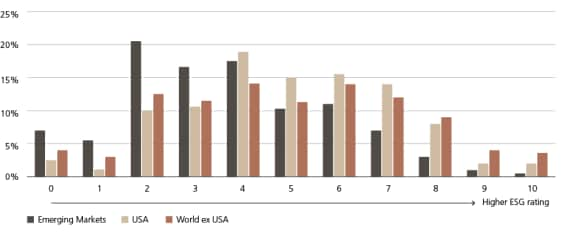
EM companies are sometimes considered laggards in sustainability, given their relatively lower average sustainability scores compared to developed markets peers.
From our experience, however, these lower scores are often less due to actual performance differences and more a reflection of lower levels of public, English language disclosure of traditional sustainability metrics. For example, in carbon dioxide emissions disclosures - the most frequently reported ESG metric among MSCI ACWI constituents - 68% of developed markets companies report Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions figures, compared to below 45% of EM companies.
Distribution of industry-adjusted ESG scores for three sub-regions
Distribution of industry-adjusted ESG scores for three sub-regions
Sustainable leaders outperform, and particularly in EM
Sustainable leaders outperform, and particularly in EM
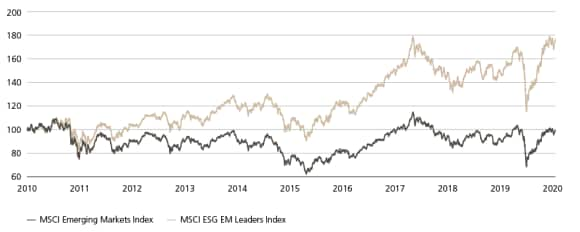
The most basic measure of ESG performance, the MSCI ESG EM Leader Index, has demonstrated that companies with top ESG scores significantly out-performed over the past decade, generating 3.09% of annualized out-performance against MSCI EM index since 2010. The MSCI ESG EM Leader Index selects companies with the top 50% of ESG scores within each sector of the MSCI EM Index.
A study by MSCI "How Markets Price ESG: Have Changes in ESG Scores Affected Stock Prices?” demonstrated that from 2013-2017, companies with improving ratings have outperformed the benchmark globally by 0.97% returns annually, this outperformance in EM was higher, at 2.88% annually.
This is also borne out by our experience wherein good quality companies - ESG being one component of quality - tend to outperform poor quality ones over the medium to long term.
Identifying improvers
Identifying improvers
Given the lower levels of public English language disclosure of traditional sustainability metrics in EM, there is greater need for primary research on EM companies from an ESG perspective including regular interactions with management and other stakeholders. This helps to supplement data and ESG scores/ratings from third-party providers, and allows for an informed judgement on the fundamentals and sustainability practices of a company.
In addition this can lead to opportunities to engage with the companies and encourage them to improve in their practices. This can not only lead to better ESG scores and ratings for the company but also have a positive impact on their long-term financial performance.
MSCI Emerging Markets Index & MSCI ESG EM Leaders Index, Jan 1, 2010 - Oct, 11, 2020
MSCI Emerging Markets Index & MSCI ESG EM Leaders Index, Jan 1, 2010 - Oct, 11, 2020
Find out more about our latest emerging market equites portfolio with a sustainable focus.
